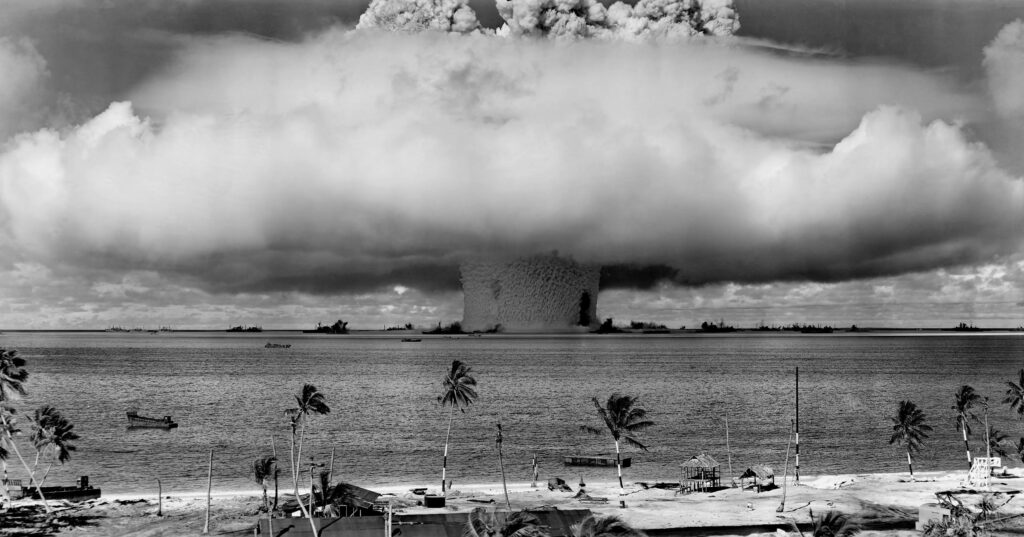
Introduction of C38 atomic bomb
The C38 atomic bomb stands as a significant development in the history of nuclear weapons. This article delves into its origins, technical specifications, impact, and broader implications, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of this powerful device.
The Birth of Nuclear Weaponry
The advent of nuclear weapons dates back to the Manhattan Project during World War II, where scientists and military experts collaborated to create the first atomic bombs. These efforts culminated in the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, which demonstrated the devastating potential of nuclear technology.
Development of the C38
The C38 atomic bomb emerged from subsequent advancements in nuclear weaponry. It was developed during the Cold War, a period marked by intense rivalry and arms races between the United States and the Soviet Union. This era saw rapid advancements in military technology, with both superpowers striving to outdo each other.
Technical Specifications
The C38 atomic bomb is characterized by its unique technical specifications. It utilizes enriched uranium or plutonium as its core, which undergoes nuclear fission to release a tremendous amount of energy. The design focuses on maximizing the efficiency and yield of the explosion.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action in the C38 involves initiating a nuclear chain reaction. When the bomb is detonated, conventional explosives compress the nuclear material to a supercritical state, triggering a rapid release of energy. This process results in an explosive force that can cause widespread destruction.
Yield and Destructive Power
One of the most critical aspects of any atomic bomb is its yield, measured in kilotons or megatons of TNT. The C38 has a substantial yield, capable of causing massive destruction over a wide area. Its power surpasses many earlier models, reflecting the advancements in nuclear technology.
Delivery Systems
The delivery systems for the C38 atomic bomb include intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), strategic bombers, and submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs). These platforms provide versatility in deployment, ensuring the bomb can reach its target with precision.
Strategic Importance
The strategic importance of the C38 lies in its role as a deterrent. During the Cold War, the doctrine of Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD) hinged on the capability to inflict unacceptable damage on an adversary. The C38 played a crucial role in maintaining this balance of power.
Ethical and Moral Considerations
The development and potential use of the C38 atomic bomb raise significant ethical and moral considerations. The immense destructive power of nuclear weapons poses questions about their justification, humanitarian impact, and the long-term consequences for humanity.
Political Implications
The existence of the C38 atomic bomb has profound political implications. It influences international relations, arms control agreements, and non-proliferation efforts. Nations with nuclear capabilities wield significant influence on the global stage, shaping geopolitical dynamics.
Non-Proliferation Efforts
Efforts to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons have been ongoing since the inception of atomic bombs. Treaties such as the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) aim to limit the number of nuclear-armed states and promote disarmament. The C38 is a focal point in these discussions.
The Role of Science and Technology
Advancements in science and technology have been integral to the development of the C38 atomic bomb. Innovations in physics, engineering, and material science have enabled the creation of more efficient and powerful nuclear weapons.
Environmental Impact
The detonation of C38 atomic bomb, including the C38, has significant environmental consequences. Radioactive fallout, atmospheric contamination, and long-term ecological damage are some of the adverse effects associated with nuclear explosions.
Health Effects
Exposure to radiation from nuclear explosions can have severe health effects. Acute radiation sickness, increased cancer risk, and genetic damage are some of the health issues faced by populations exposed to nuclear fallout.
Historical Incidents
Throughout history, there have been several incidents involving C38 atomic bomb. These range from testing in remote locations to accidental releases of nuclear material. Each incident underscores the inherent risks associated with nuclear weapons.
Disarmament Movements
Disarmament movements have gained momentum over the decades, advocating for the reduction and elimination of nuclear arsenals. Organizations and activists call for treaties and policies that promote global security without reliance on nuclear deterrence.
The Role of Diplomacy
Diplomacy plays a crucial role in managing nuclear threats and promoting disarmament. Diplomatic efforts focus on building trust, verifying compliance with treaties, and fostering international cooperation to address nuclear challenges.
The Future of Nuclear Weapons
The future of nuclear weapons, including the C38, is uncertain. Technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving security threats will shape the trajectory of nuclear arsenals and the policies governing their use.
Public Perception
Public perception of nuclear weapons has evolved over time. Awareness of their destructive potential and the humanitarian consequences has fueled anti-nuclear sentiment and calls for disarmament.
Cultural Depictions
Nuclear weapons, including the C38, have been depicted in various cultural mediums, such as films, literature, and art. These depictions reflect societal fears, ethical dilemmas, and the impact of nuclear weapons on human civilization.
Scientific Research
Ongoing scientific research continues to explore the implications of nuclear weapons. Studies on radiation effects, environmental impact, and alternative energy sources contribute to a broader understanding of the consequences and alternatives to nuclear technology.
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness efforts are vital in promoting understanding of nuclear issues. Programs and initiatives aim to inform the public, policymakers, and future generations about the risks and responsibilities associated with nuclear weapons.
International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential in addressing the challenges posed by nuclear weapons. Collaborative efforts in arms control, disarmament, and non-proliferation contribute to global security and stability.
Technological Safeguards
Technological safeguards are implemented to prevent accidental or unauthorized use of nuclear weapons. These include secure communication systems, fail-safe mechanisms, and rigorous command and control protocols.
Conclusion
The C38 atomic bomb represents a critical juncture in the history of nuclear weapons. Its development, implications, and the ongoing efforts to manage and mitigate the associated risks underscore the complexity of the nuclear age. Understanding the C38’s role and impact is crucial in shaping a safer and more secure future for humanity.
Read Also: Understanding Tech Console DefStartup – A Comprehensive Guide 2024